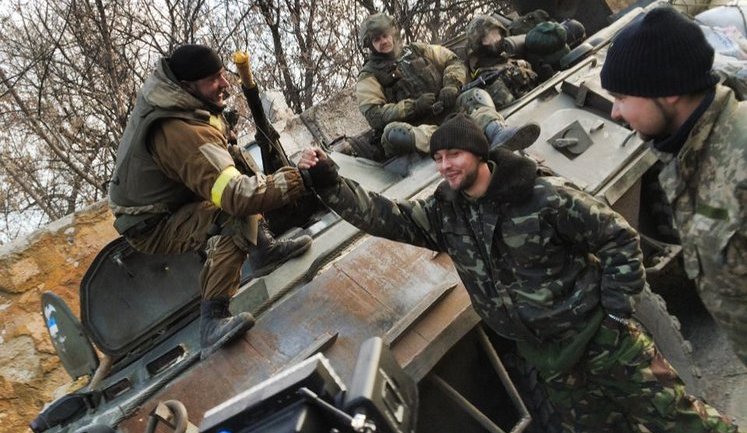
Rotation is an essential military strategy ensuring that soldiers serving for extended periods receive rest, thus maintaining the efficiency and morale of the armed forces. Recently, Ukrainian soldiers have been rotated out after holding positions for extended periods, such as the soldiers from the 24th Mechanized Brigade returning after 75 days. Meanwhile, in regions like Vovchansk and Dvorichna, Russian forces are actively rotating their units, indicating strategic regrouping. The Ukrainian Ministry of Defense has also introduced a mechanism for systematic rotation allowing soldiers rest after 90 days of active combat, improving resilience on the front lines. Such efforts are crucial in sustaining prolonged military engagements and preparing troops effectively for ongoing and future operations.
What is the importance of rotating military troops?
Rotation ensures the well-being and continued effectiveness of military personnel. By periodically replacing troops on the front lines, soldiers get necessary rest and respite, which helps decrease combat fatigue and maintain high morale. This process is crucial for prolonged conflicts where sustained troop efficiency is needed.
How long do Ukrainian soldiers typically serve before rotation?
Ukrainian soldiers may serve varying lengths before rotation. According to recent updates from the Ministry of Defense, a new rotation mechanism allows soldiers rest after 90 days of continuous combat service. This approach helps reduce fatigue and ensures readiness among the troops.
What are the implications of Russian troop rotations near Ukraine?
Russian troop rotations in regions near Ukraine, such as Vovchansk and Dvorichna, suggest strategic repositioning or reinforcement of their forces. These movements might be intended to prepare for potential escalations or to optimize their current operational capabilities in these contested areas.
How does the rotation mechanism impact Ukrainian military morale?
The rotation mechanism positively impacts military morale by providing soldiers with scheduled periods for rest and recovery. This is especially important in prolonged conflicts to prevent burnout and maintain operational effectiveness, ensuring that forces remain motivated and ready for engagement.
What challenges exist regarding troop rotation in Ukraine?
Challenges to troop rotation in Ukraine include logistical constraints, the intensity of ongoing operations, and ensuring that new rotations adequately cover frontline needs without compromising defense capabilities. Balancing these elements is essential to maintain national security and combat readiness.