The occupation of Crimea remains a critical geopolitical issue in 2025, with ongoing international debates and military actions. Notably, OSCE President Pere Juan Pons Sampietro has emphasized the illegal nature of the Russian occupation and the need for the release of detained OSCE representatives. EU sanctions against Russia have been extended, indicating enduring regional tension. Additionally, the U.S. discussions around recognizing Crimea as Russian territory highlight diplomatic complexities. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy reaffirmed Ukraine's stance against such recognition. Military activities continue, with Russia reinforcing defenses in occupied Crimea, highlighting the strategic significance of the region. These developments underscore the enduring and evolving challenges associated with Crimea's occupation.
What is the current status of Crimea in 2025?
As of 2025, Crimea remains under Russian occupation since 2014. The international community, including the EU and Ukraine, does not recognize this occupation. Military tensions and diplomatic efforts continue regarding the peninsula.
Has the EU extended sanctions against Russia for its actions in Crimea?
Yes, the EU has extended sanctions against Russia for the illegal annexation of Crimea until June 23, 2026. These sanctions aim to pressure Russia to respect Ukraine's sovereignty and borders.
What are the implications of Russia's military actions in Crimea?
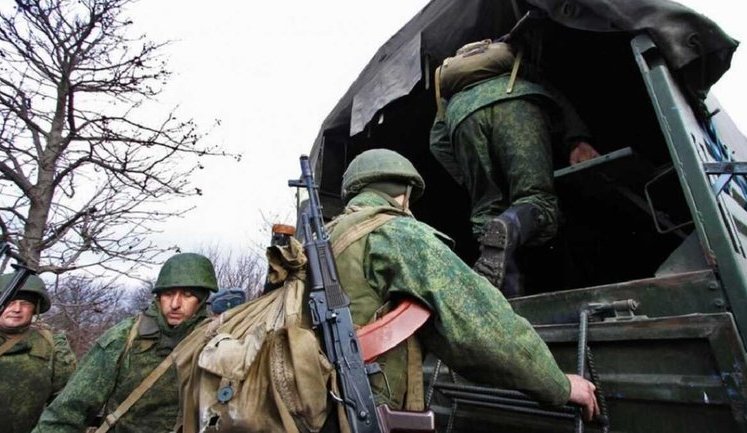
Russia's military activities in Crimea involve strengthening air defenses and building naval capabilities. These actions are strategic, ensuring military control over the occupied territory and enhancing defensive readiness in the Black Sea region.
How have global leaders responded to the situation in Crimea?
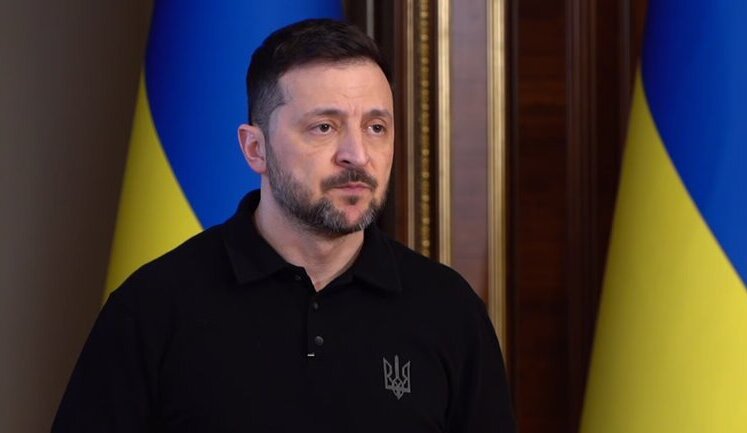
Global leaders have expressed diverse views on Crimea. President Zelenskyy of Ukraine maintains the stance that Crimea is Ukrainian, while discussions in the US, led by President Trump, have explored recognizing the occupation, complicating international diplomacy.
What was discussed in recent international events regarding Crimea?
At recent international events, Ukraine's territorial integrity was a central theme. The OSCE and other bodies called for the release of detainees and rejected the Russian occupation. Military strategies and diplomatic paths are being explored continually.
Has there been any attempt to negotiate a resolution for the Crimea issue?
Attempts to negotiate a resolution have included discussions of recognizing Crimea's status but remain controversial. Ukraine stands firm against recognition, while diplomatic efforts seek a peaceful resolution that respects international law.
What role does the United States play in the Crimea situation?
The United States has been involved in discussions about potentially recognizing Crimea's occupation as part of a broader peace deal with Russia. This proposal has been divisive, impacting international relations and negotiations.
What steps has Ukraine taken regarding Crimea since the occupation began?
Since the occupation began, Ukraine has remained committed to reclaiming Crimea. President Zelenskyy and government officials continue to engage in diplomatic efforts and have reinforced the need for military and political strategies to address the occupation.