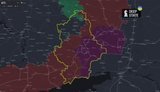
In 2025, the Russian occupation of Ukraine expanded significantly with approximately 4,300 square kilometers being captured. The occupation impacts numerous regions, including Sumy, Donetsk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia. As Russian forces maintain control over these territories, issues of human rights violations persist, highlighted by the UN's resolution condemning such actions. Ukrainian efforts to reclaim occupied territories and bring back displaced children continue, evidenced by the successful evacuation of multiple groups. The President's initiative, Bring Kids Back UA, plays a crucial role in these endeavors. Meanwhile, the geopolitical tensions rise as international bodies like the OSCE remain actively involved in mediation attempts to restore peace and resolve humanitarian issues in the occupied regions of Ukraine.
What is the current status of the Russian occupation in Ukraine?
The Russian occupation in Ukraine has expanded significantly in 2025, with over 4,300 square kilometers of territory under control. This occupation affects areas such as Sumy, Donetsk, and Kherson, with significant geopolitical and humanitarian implications, including widespread human rights violations and disrupted local governance.
How has the occupation affected human rights in Ukraine?
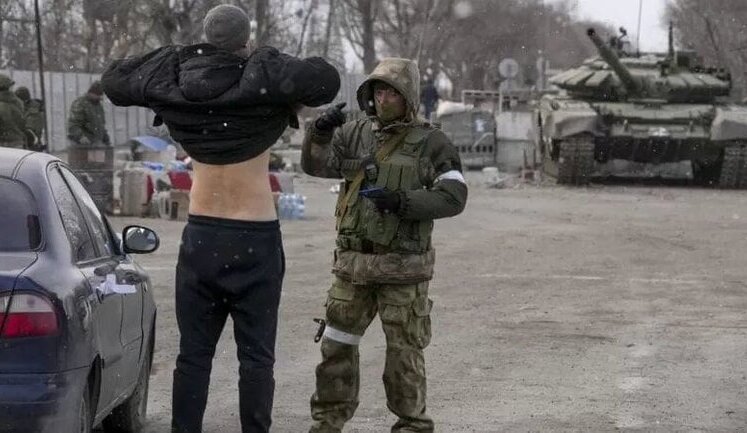
The occupation has led to numerous human rights violations, including forced seizures of property, restrictions on freedom of movement, and suppression of civil liberties. The UN General Assembly has adopted resolutions condemning these violations as it remains a significant concern affecting civilian populations in occupied regions.
What are the humanitarian efforts being made amidst the occupation?
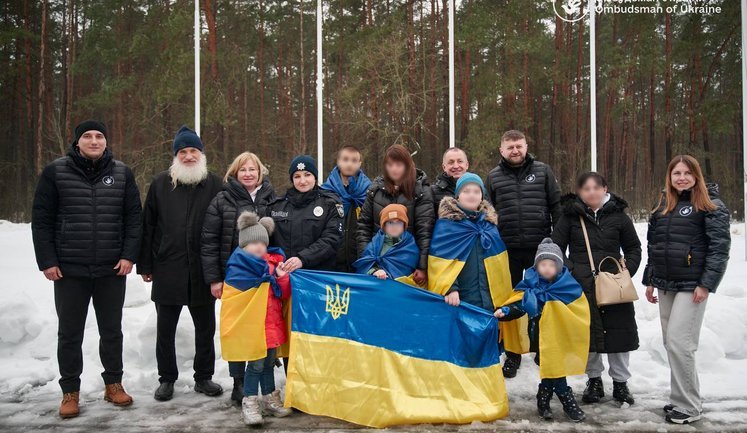
Humanitarian efforts, particularly focusing on the evacuation of children and families from occupied regions, are ongoing. The Ukrainian President's initiative, Bring Kids Back UA, has successfully rescued numerous children from occupied territories, providing them with safety, medical care, and psychological support upon their return to Ukrainian-controlled areas.
How has the international community responded to the situation?
The international community, including bodies like the UN and OSCE, has responded with resolutions and calls for mediation to address human rights abuses and work towards a peaceful resolution. However, the geopolitical complexities and Russian military actions pose challenges to effective intervention.
What are the geopolitical consequences of the occupation?
The occupation exacerbates geopolitical tensions in the region, impacting Ukraine's sovereignty and regional stability. The ongoing conflict affects international relations, drawing responses from global entities and influencing diplomatic engagements focused on conflict resolution and peace efforts.
Are elections possible in the occupied territories of Ukraine?
According to President Volodymyr Zelenskyy, elections cannot proceed in territories occupied by Russia, as the occupation undermines democratic processes and local governance, creating an environment that lacks the necessary conditions for fair and free electoral practices.
What regions in Ukraine have come under occupation in 2025?
In 2025, multiple regions have come under occupation, notably Sumy, Donetsk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia. Russian military advances in these areas have led to control over strategic locations, contributing to significant territorial changes in the ongoing conflict.
What impact has the occupation had on the economy in the affected regions?
The occupation severely impacts local economies as businesses cease operations and resources become scarce. Employment rates plummet, exacerbating economic instability and hardships for residents amid the ongoing conflict and territorial occupation by Russian forces.
How are the occupied territories being managed by Russian forces?
Russian forces implement strict control in occupied territories, with enforced seizure of properties and restrictions on civilian movements. Authorities have been given explicit rights by the Russian government to maintain this control until 2030, further complicating the return to normalcy for affected populations.