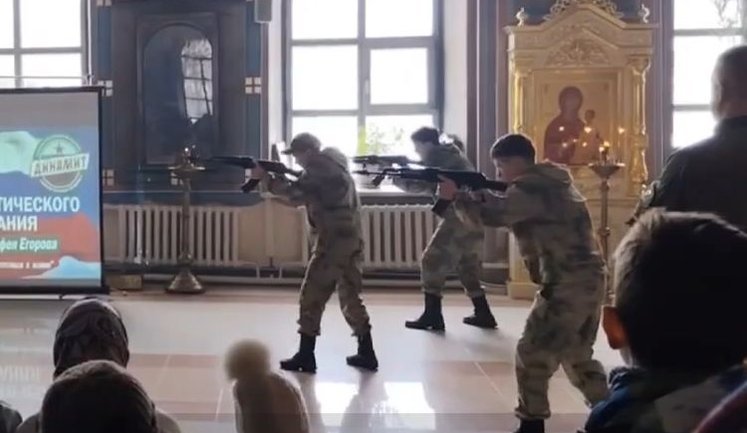
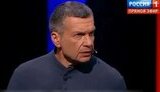
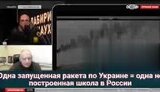
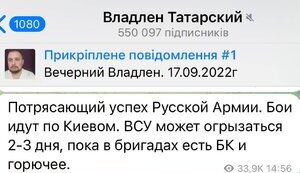
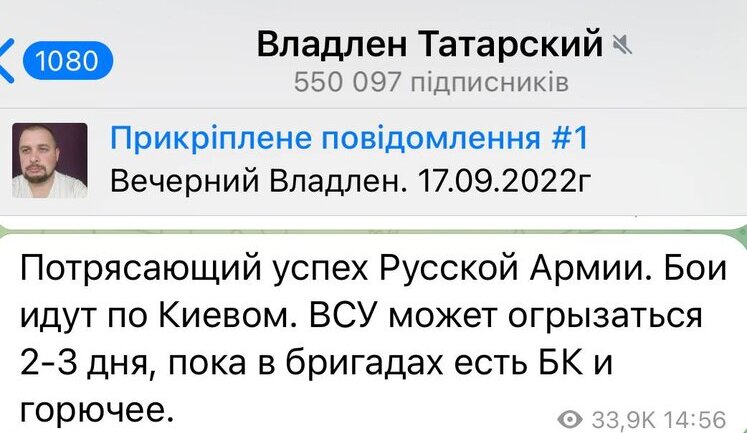
Propaganda plays a pivotal role in the Kremlin's strategy, influencing narratives in Ukraine and globally. Prominent propagandists like Solovyov openly call for extreme actions, including nuclear strikes on Europe. Such rhetoric underscores Russia's aggressive information warfare tactics. In occupied territories, propaganda efforts aim to justify military actions and demonize Ukraine. Meanwhile, allegations surface of Kremlin-led ethnic cleansing plans in eastern Ukraine, with propagandists advocating the forcible removal of civilians. To counter potential Western influence, propaganda narratives are tailored to portray Russia as a defender of national interests, often targeting US policies with AI-driven misinformation. This complex propaganda ecosystem significantly impacts public perception, both internationally and within Russia.
How does Kremlin propaganda impact the war in Ukraine?
Kremlin propaganda significantly influences narratives about the war in Ukraine. It aims to demonize Ukrainian authorities and justify military actions. By spreading misinformation and fabricated stories, it seeks to manipulate public perception both in Russia and internationally, contributing to false narratives that justify aggression and support for the conflict.
What are the main themes of Russian propaganda related to Ukraine?
Russian propaganda concerning Ukraine often focuses on themes such as the alleged need to "denazify" the country, claims of protecting Russian-speaking populations, and portraying the Ukrainian government as illegitimate. These narratives are used to justify military interventions and demonize Ukraine to both Russian citizens and the international audience.
How are propaganda tactics evolving in the conflict?
Propaganda tactics have evolved to include sophisticated disinformation campaigns using digital and social media platforms. The use of AI to generate false narratives and the creation of seemingly legitimate reports filled with misleading information are prominent. This evolution reflects an adaptive strategy to influence public opinion and counter opposing viewpoints effectively.
What role does AI play in Russian propaganda efforts?
AI plays a crucial role in advancing Russian propaganda by enabling the creation and dissemination of large-scale disinformation campaigns. It allows for the generation of deepfake technologies, automated bots spreading Russian narratives on social media, and the rapid production of fake articles that portray misleading facts as truth. This technological edge enhances the efficiency and reach of propaganda.
How do propaganda efforts justify the Kremlin’s political and military actions?
Propaganda is used to create narratives that justify the Kremlin's actions by portraying them as necessary for regional stability and security. It often involves highlighting threats posed by NATO or nationalistic movements within Ukraine, framing Russia's military actions as defensive rather than aggressive. This narrative seeks to rationalize political and military decisions internally and to international observers.
What measures are being taken to counter Russian propaganda?
Countries affected by Russian propaganda are employing various measures, including strengthening media literacy among their populations, implementing sanctions against key propagandists and media outlets, and using technology to detect and flag disinformation campaigns. These efforts aim to educate the public and diminish the influence of Kremlin-led narratives.
Are there international sanctions targeting Russian propagandists?
Yes, international sanctions have been imposed targeting Russian propagandists. These measures include asset freezes and travel bans against individuals and entities involved in disseminating propaganda. Sanctions aim to disrupt their operations and send a clear message about the unacceptability of their actions in supporting aggression and misinformation.